Map - TreeMap 源码解析
Map - TreeMap 源码解析
介绍
TreeMap 和 HashMap 类似,都是 Map 接口的一个实现类,是一个能够存储 <K,V> 键值对的集合。与 HashMap 相比,其底层是存储 <K,V> 结点的一个红黑树,能自动对添加进来的元素节点进行排序,默认按照元素 Key 的自然顺序进行排列,也可在构造时传入比较器。
TreeMap 具有如下特点:
- 不允许出现重复的 Key
- 可以插入 null 键,null 值,但仅能一个 Key 为 null
- 可以对元素进行排序
- 无序集合,即插入顺序和其存储、遍历顺序不一致
常用API
- 新增元素:put()
- 获取指定K元素:get(K k)
- 遍历元素:entrySet()
- 获取所有的Key:keySet()
- 获取所有的Value:values()
- 删除元素:remove()
- 清空元素:clear()
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] agrs){
//创建TreeMap对象:
TreeMap<String,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<String,Integer>();
System.out.println("初始化后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size());
//新增元素:
treeMap.put("hello",1);
treeMap.put("world",2);
treeMap.put("my",3);
treeMap.put("name",4);
treeMap.put("is",5);
treeMap.put("jiaboyan",6);
treeMap.put("i",6);
treeMap.put("am",6);
treeMap.put("a",6);
treeMap.put("developer",6);
System.out.println("添加元素后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size());
//遍历元素:
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet = treeMap.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : entrySet){
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("TreeMap元素的key:"+key+",value:"+value);
}
//获取所有的key:
Set<String> keySet = treeMap.keySet();
for(String strKey:keySet){
System.out.println("TreeMap集合中的key:"+strKey);
}
//获取所有的value:
Collection<Integer> valueList = treeMap.values();
for(Integer intValue:valueList){
System.out.println("TreeMap集合中的value:" + intValue);
}
//获取元素:
Integer getValue = treeMap.get("jiaboyan");//获取集合内元素key为"jiaboyan"的值
String firstKey = treeMap.firstKey();//获取集合内第一个元素
String lastKey =treeMap.lastKey();//获取集合内最后一个元素
String lowerKey =treeMap.lowerKey("jiaboyan");//获取集合内的key小于"jiaboyan"的key
String ceilingKey =treeMap.ceilingKey("jiaboyan");//获取集合内的key大于等于"jiaboyan"的key
SortedMap<String,Integer> sortedMap =treeMap.subMap("a","my");//获取集合的key从"a"到"jiaboyan"的元素
//删除元素:
Integer removeValue = treeMap.remove("jiaboyan");//删除集合中key为"jiaboyan"的元素
treeMap.clear(); //清空集合元素:
//判断方法:
boolean isEmpty = treeMap.isEmpty();//判断集合是否为空
boolean isContain = treeMap.containsKey("jiaboyan");//判断集合的key中是否包含"jiaboyan"
}
}底层实现
TreeMap 继承于 AbstractMap 抽象类,而 AbstractMap 又实现了 Map 接口,为其子类的继承提供了便利。
TreeMap 间接性的实现了 Map 接口,故其存储的是 <K,V> 格式的键值对数据。实现了 Cloneable 接口中的 clone() 方法,故其能够被克隆。还实现了 Java.io.Serializable 接口,故其能够被序列化。
特别的 TreeMap 实现了一个 NavigableMap 接口,具体该接口的关系图如下:
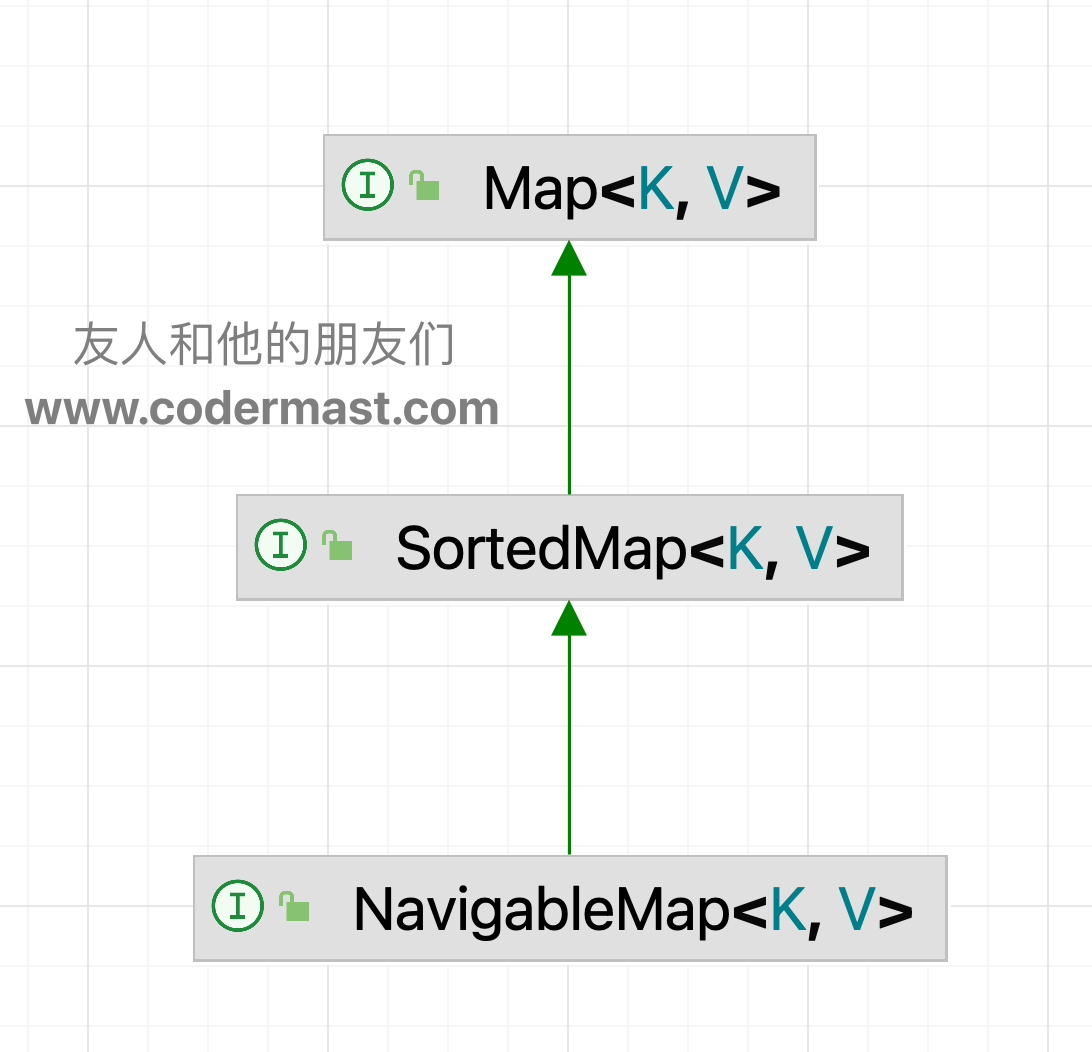
该接口继承了 SortedMap 接口,从字面上来看,实现该接口的 Map 都有排序功能,主要是因为 SortedMap 接口内定义了一个 comparator 方法,有了该方法就能对集合内的元素进行排序。
Comparator<? super K> comparator()另外 NavigableMap 接口中还定义了一些对集合内元素查找的方法,具体如下所示:
NavigableMap接口源码
public interface NavigableMap<K,V> extends SortedMap<K,V> {
// 返回键小于指定 key 的第一个元素(Map.Entry),如果不存在则返回 null。
Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key);
// 返回键小于指定 key 的第一个键,如果不存在则返回 null。
K lowerKey(K key);
// 返回键小于等于指定 key 的第一个元素(Map.Entry),如果不存在则返回 null。
Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key);
// 返回键小于等于指定 key 的第一个键,如果不存在则返回 null。
K floorKey(K key);
// 返回键大于等于指定 key 的第一个元素(Map.Entry),如果不存在则返回 null。
Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key);
// 返回键大于等于指定 key 的第一个键,如果不存在则返回 null。
K ceilingKey(K key);
// 返回键大于指定 key 的第一个元素(Map.Entry),如果不存在则返回 null。
Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key);
// 返回键大于指定 key 的第一个键,如果不存在则返回 null。
K higherKey(K key);
// 返回集合中的第一个元素(Map.Entry),如果不存在则返回 null。
Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry();
// 返回集合中的最后一个元素(Map.Entry),如果不存在则返回 null。
Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry();
// 返回并移除集合中的第一个元素(Map.Entry),如果不存在则返回 null。
Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry();
// 返回并移除集合中的最后一个元素(Map.Entry),如果不存在则返回 null。
Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry();
// 返回此映射的逆序视图。
NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap();
// 返回此映射中键的逆序视图。
NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet();
// 返回此映射中键的逆序视图(NavigableSet)。
NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet();
// 返回此映射的部分视图,其键的范围从 fromKey 到 toKey。
// 如果 fromInclusive 为 true,则包含 fromKey;如果 toInclusive 为 true,则包含 toKey。
NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive);
// 返回此映射的部分视图,其键小于(或等于,如果 inclusive 为 true)给定的 toKey。
NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive);
// 返回此映射的部分视图,其键大于(或等于,如果 inclusive 为 true)给定的 fromKey。
NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive);
// 返回此映射的部分视图,其键的范围从 fromKey 到 toKey。
// 注意:这些方法返回的是 SortedMap,而非 NavigableMap,因此不提供导航功能。
SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey);
SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey);
SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey);
}NavigableMap 的目的主要是为了将对集合内元素的搜索、获取功能抽取出来,并进行增强和标准化,当子类实现其接口时,自动获得以上能力。
获取元素
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}添加元素
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}删除元素
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
public void clear() {
modCount++;
size = 0;
root = null;
}排序功能
正如前面所说,TreeMap 具有排序功能,默认是通过 键 的自然顺序排列,也可传入自定义的比较器,根据比较器规则排序。
需要注意的是,只能在创建 TreeMap 对象时通过构造器方法进行传入,这是因为一旦定义好了 TreeMap 对象,其中如果已经有元素,此时再添加或修改比较规则,会造成排序功能失效。
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}现在 TreeMap 有了比较器,知道是如何比较的,但是其底层是红黑树,又是具体怎么实现存储上的排序呢?
想要理解如何存储,就必须先了解红黑树,红黑树是一种特殊处理的二叉排序树,切记红黑树不是平衡二叉树。
红黑树
具体关于红黑树的内容,红黑树的特点、如何保证其有序、左旋转、右旋转规则等知识,请移步
// TODO:「408」数据结构——红黑树详解 。
既然红黑树是二叉排序树,那么其天然有序,只需要根据其排序规则进行不断调整即可,这里由于篇幅限制就不过多赘述。
调整好以后是一棵左右子树高度差不超过2倍的二叉排序树,通过中序遍历,即可得到按序遍历结果。
二叉排序树、二叉搜索树、二叉查找树有什么区别?
三者是统一概念的不同叫法,没有任何区别。
